Latest News
-

 982018-04-29
982018-04-29Google Cloud Platform announces new credits program for researchers
Using Google Cloud Platform (GCP), researchers are accelerating breakthroughs and asking new questions they could never have asked before. Now GCP will be available to even more academic researchers through the new GCP research credits program.
-

 962018-04-27
962018-04-27Scientists discover how to harness the power of quantum spookiness by entangling clouds of atoms
Experiment produces thousands of entangled atoms, raising hopes that we can soon create real quantum computers.
-

 432018-04-11
432018-04-11Scientists Fix Genetic Risk Factor for Alzheimer’s Disease in Human Brain Cells
New insights into how a gene causes damage could impact future drug development
-

 432018-04-10
432018-04-10Machine learning offers new way of designing chiral crystals
Engineers and chemists at Hiroshima University successfully used the same technology at the core of facial recognition to design chiral crystals. This is the first study reporting the use of this technology, called logistic regression analysis, to predict which chemical groups are best for making chiral molecules.
-

 462018-03-28
462018-03-28Knitting electronics with yarn batteries
When someone thinks about knitting, they usually don't conjure up an image of sweaters and scarves made of yarn that can power watches and lights. But that's just what one group is reporting … they have developed a rechargeable yarn battery that is waterproof and flexible. It also can be cut into pieces and still work.
-

 1052018-03-11
1052018-03-11Houston Methodist Researcher Makes Bold Move by Releasing Nanotech ‘Recipe’
In a rare move, a Houston Methodist researcher is sharing his recipe for a new, more affordable way to make nanoparticles.
-
 1192018-03-01
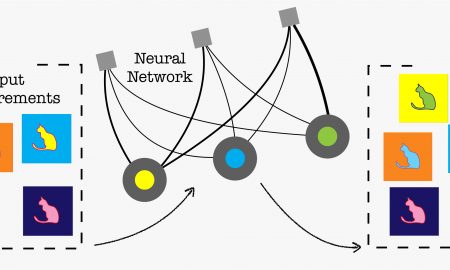
1192018-03-01Artificial Intelligence Techniques Reconstruct Mysteries of Quantum Systems
New machine learning techniques can help experimentalists probe systems of particles exponentially faster than conventional, brute-force techniques
-

 462018-02-13
462018-02-13Scope of nanotechnology widens in 2018
There's miniaturization, and then there's nanotechnology. Global markets are growing and multiplying for both. But it's the point of nanotech to effect desired technical solutions and outcomes with ever-smaller - much, much smaller - building blocks of materials.
-

 472018-02-05
472018-02-05A salamander with a genome 10 times the size of ours regrows lost limbs
Most of the extra DNA appears to be irrelevant to regeneration.
-

 1542018-01-25
1542018-01-25An AI for AI: New Algorithm Poised to Fuel Scientific Discovery, NVIDIA blogs
Deep learning is poised to fire up scientific discovery, thanks to a new algorithm that automatically generates neural networks.
-

 472018-01-13
472018-01-13Advances in Quantum and Neuromorphic Computing Research
Intel announced two major milestones in its efforts to research and develop future computing technologies including quantum and neuromorphic computing, which have the potential to help industries, research institutions and society solve problems that currently overwhelm today’s classical computers.
-

 462018-01-11
462018-01-1112-year-old wins $25,000 for an invention that helps detect lead in water
Twelve-year-old scientist Gitanjali Rao has been inventing since she was in kindergarten. Rao says that she has more than eight inventions, but it was Tethys — a 3D printed device that harnesses carbon nanotubes and a mobile app to test water for lead contamination in as little as 10 seconds










