News
-

 119
119French Regulators Approve Human Trial of a Bionic Eye
Pixium Vision receives approval from French regulators to conduct feasibility study of its PRIMA sub-retinal implant
-

 140
140CRISPR 2.0 Is Here, and It’s Way More Precise
It could one day be used to treat a range of inherited diseases.
-

 119
119Cancer-Targeted Nanoparticles Become Temperature “Intelligent”
Thermal self-regulating nanoparticles that seek out and destroy cancer cells may sound like something pulled from the new Blade Runner movie script, but researchers at the University of Surrey have developed the therapy for use today.
-

 120
120Single nanoparticle mapping paves the way for better nanotechnology
Researchers at Chalmers University of Technology and the Technical University of Denmark have developed a method that makes it possible to map the individual responses of nanoparticles in different situations and contexts.
-

 113
113Quantum machine goes in search of the Higgs boson
D-Wave system shows quantum computers can learn to detect particle signatures in mountains of data, but doesn't outpace conventional methods - yet.
-

 139
139Decoding the Origin of Universe’s Heavy Elements in the Light from a Neutron Star Merger
On Aug. 17, scientists were treated to detections confirming the first measurement of a neutron star merger and its explosive aftermath.
-

 134
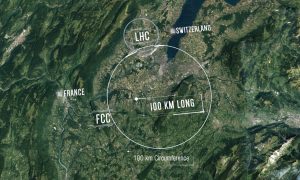
134Canadian teens hunt subatomic particles at CERN after winning global contest
A group of teenaged students from Cambridge, Ont., is hunting for new subatomic particles at the home of the world's largest atom smasher this week. They hope to turn up what particle physics PhDs have been unable find after decades of searching.
-

 345
345New Cyberattack Could Take Out Solar Arrays
Renewable energy may have a cybersecurity problem. At the recent BlackHat security conference, researchers found that it was possible to hack into the software that controls many wind farms, and potentially take the turbines hostage. Now it looks like solar panels are vulnerable, too.
-
 321
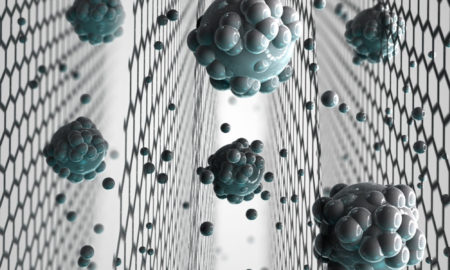
321Graphene sieve turns seawater into drinking water
Graphene-oxide membranes have attracted considerable attention as promising candidates for new filtration technologies. Now the much sought-after development of making membranes capable of sieving common salts has been achieved.
-
 135
135Bringing cryopreserved tissue back to life using “nano-warming” technology
The goal of new 'nano-warming' technology is to make more organs and tissue available for transplant.